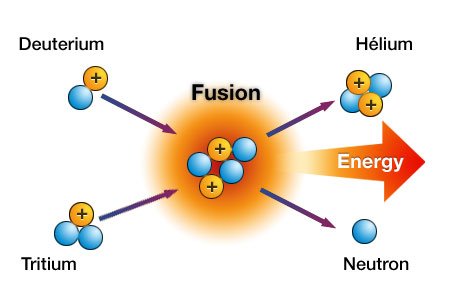
Solar energy is what reaches the Earth in the form of electromagnetic radiation from the Sun, where it is generated by a process of nuclear fusion.

In the Sun, nuclear fusion reactions take place constantly: the hydrogen atoms fuse giving rise to a helium atom, releasing a large amount of energy. The small part that reaches Earth is also partially reflected towards outer space by the presence of the Earth's atmosphere.
Solar energy reaches the surface of the Earth in two different ways:
• Inciting on the illuminated areas (direct radiation).
• By reflection of the solar radiation absorbed by the air and atmospheric dust (diffuse radiation).
• By reflection of the solar radiation absorbed by the air and atmospheric dust (diffuse radiation).
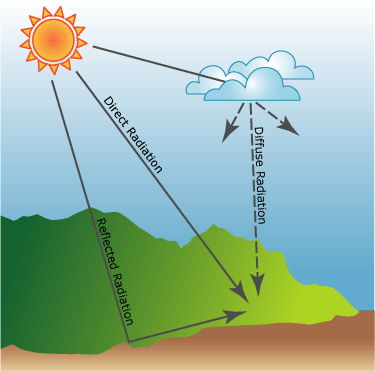
The first is usable directly. Flat collectors and photovoltaic cells take advantage of the second, to some extent.
The advantages of solar energy are:
1.-Solar energy is a practically unlimited renewable resource. There is virtually an unlimited supply of solar energy that we can use and it is a renewable energy. This means that our dependence on fossil fuels can be reduced in direct proportion to the amount of solar energy we produce. With the constant increase in demand for traditional energy sources and the consequent increase in costs, solar energy is increasingly a necessity.
2.-It does not pollute. Solar energy is an excellent source of alternative energy because there is no pollution when used.
It has a low cost of use. The only cost associated with the use of solar energy is the cost of manufacturing the components and installation. After the initial investment there are no additional costs associated with its use.
It has a low cost of use. The only cost associated with the use of solar energy is the cost of manufacturing the components and installation. After the initial investment there are no additional costs associated with its use.
3.-It is adaptable to the needs. Solar energy systems can be designed to be flexible and expandable. This means that your first solar project can be small and you can increase the capacity of your system in the future to adapt it to your needs. By starting with a relatively small project you can reduce the initial expense.
4.-Is clean. A solar energy system for electricity generation in the home can potentially remove up to 18 tons of greenhouse gas emissions into the environment each year.
5.-Solar energy operates with silent systems. No noise pollution.
6.-You find it everywhere. A great advantage of solar energy is its use in remote locations. It is the best way to provide electricity to isolated places around the world, where the cost of installing electricity distribution lines is too high.
The drawbacks of this energy source are:
1.-Large commercial-scale solar power generation projects may require large amounts of land. However, a system for a house does not have this problem.
2.-The initial costs of installing a solar energy system can be high compared to other alternatives. However, as noted in the advantages section, there are no subsequent costs, so the initial investment recovers quickly. For some families, the initial costs can be a major obstacle, so in many countries there are government supports and financing schemes.
3.-In some places sunlight does not have the intensity or is not constant enough to provide a permanent energy flow. This is practically not a problem in Mexico, since our country has an excellent capture of sunlight in practically all its territory.
2.-The initial costs of installing a solar energy system can be high compared to other alternatives. However, as noted in the advantages section, there are no subsequent costs, so the initial investment recovers quickly. For some families, the initial costs can be a major obstacle, so in many countries there are government supports and financing schemes.
3.-In some places sunlight does not have the intensity or is not constant enough to provide a permanent energy flow. This is practically not a problem in Mexico, since our country has an excellent capture of sunlight in practically all its territory.
The use of solar energy can be done in two ways: thermal and photovoltaic.
Thermal path: transforms the energy from the Sun into heat energy. This transformation can occur at low, medium and high temperature. The transformation at low temperature is used, generally, for domestic heating, room air conditioning, water heating in hospitals, swimming pools .... Flat collectors are used to house a circuit with a fluid that absorbs solar radiation and transmits it in form of heat to the heating system. These systems take advantage of solar energy at temperatures that range between 35 ºC and 90 ºC, currently being the main application of solar thermal energy in Spain.
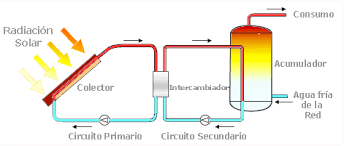
In installations that work at medium temperature, between 90 ºC and 200 ºC, they use a set of concentration collectors in different ways:
Cylindrical-parabolic: they collect solar energy and transmit it to a fluid (thermal oil) in the form of heat.

Heliostats: generally formed by steerable mirrors so that the incident radiation is reflected at a fixed point. The applications of this type of installations are mainly industrial.

High-temperature installations are thermal power plants with temperatures above 400ºC. They are formed by a large surface of heliostats supported by supports that reflect the solar radiation and concentrate it in a small receiving point. This receiver transmits solar radiation in the form of heat to a fluid (water, air, liquid metals) that circulates through a primary circuit. In a steam generator, this energy is transmitted to a second circuit, producing the water vapor capable of driving a turbine-alternator group producing the electrical energy. The performance of these facilities is approximately 20%.

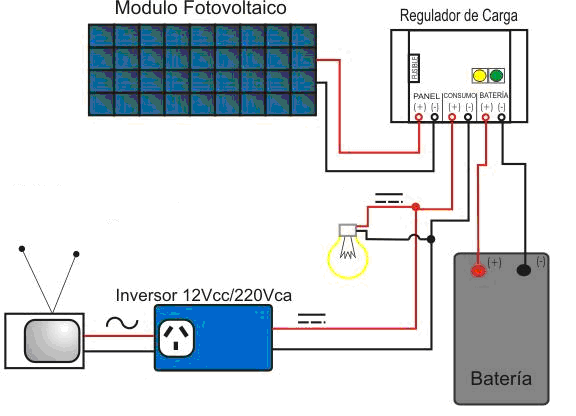
Photovoltaic conversion: solar photovoltaic systems are formed by a set of solar or photovoltaic cells arranged in panels that directly transform solar energy into electrical energy.
Sunlight transports energy in the form of a flow of photons. When these photons affect certain types of materials and under certain conditions, they cause an electric current. It is what is known as a photovoltaic effect.
Sunlight transports energy in the form of a flow of photons. When these photons affect certain types of materials and under certain conditions, they cause an electric current. It is what is known as a photovoltaic effect.
Solar or photovoltaic cells are small elements made of a doped semiconductor crystalline element, silicon-germanium (Si-Ge). Upon impacting them, the photons produce a movement of electrons inside the cell and appear between their ends a difference of potential that makes them a small electrical generator. The current cost of these cells is very high, their performance is low (10-15%) and their production is very polluting.
The development of these systems is linked to the technique of artificial satellites. In a first stage, due to the reliability of its operation, its reduced weight and its scarce maintenance needs, these systems were used to cover the energy needs of the satellites.
The technological development strives to improve the performance of these systems and reduce their cost to make them economically viable.
If you want to try This your home click SunRayEnergy






